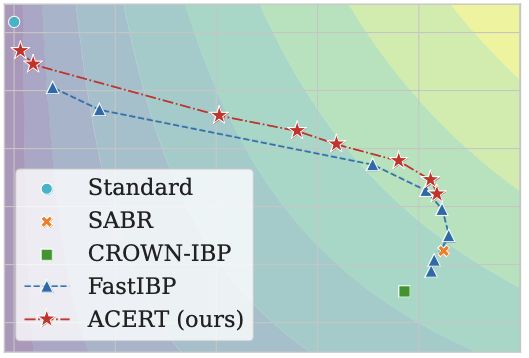
 | Z. Nurlanov, F. R. Schmidt, F. Bernard In: European Conference on Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases (ECML PKDD), 2024. [pdf] [code] @article{nurlanov24,
title = {Adaptive Certified Training: Towards Better Accuracy-Robustness Tradeoffs},
author = {Z. Nurlanov and F. R. Schmidt and F. Bernard},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.13078},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-09-09},
urldate = {2024-09-09},
journal = {European Conference on Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases (ECML PKDD)},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|
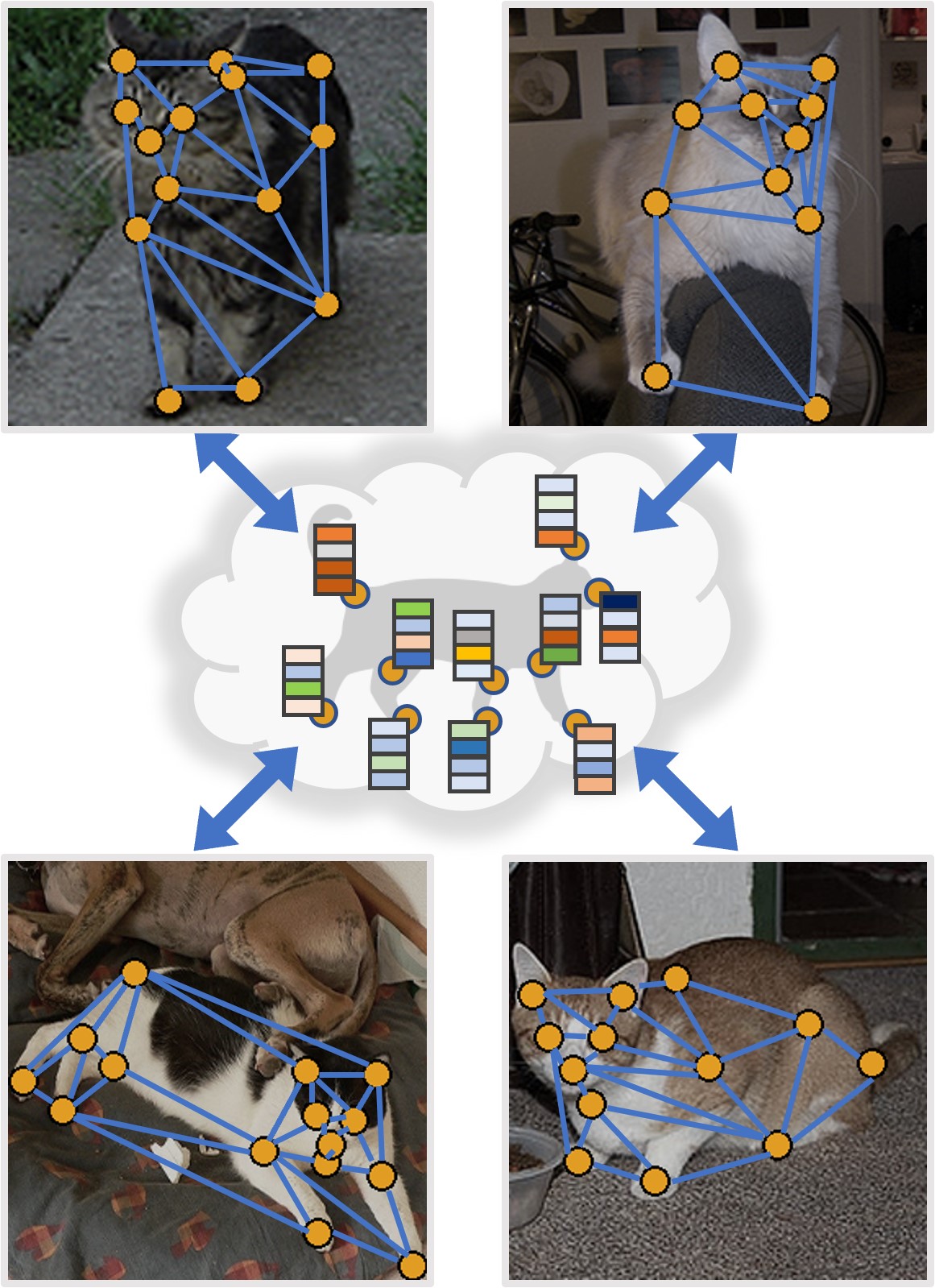 | Z. Nurlanov, F. R. Schmidt, F. Bernard In: AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2023. [pdf]
@article{nurlanov2023,
title = {Universe Points Representation Learning for Partial Multi-Graph Matching},
author = {Z. Nurlanov and F. R. Schmidt and F. Bernard },
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.00780},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-02-07},
urldate = {2023-02-07},
journal = {AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
abstract = {Many challenges from natural world can be formulated as a graph matching problem. Previous deep learning-based methods mainly consider a full two-graph matching setting. In this work, we study the more general partial matching problem with multi-graph cycle consistency guarantees. Building on a recent progress in deep learning on graphs, we propose a novel data-driven method (URL) for partial multi-graph matching, which uses an object-to-universe formulation and learns latent representations of abstract universe points. The proposed approach advances the state of the art in semantic keypoint matching problem, evaluated on Pascal VOC, CUB, and Willow datasets. Moreover, the set of controlled experiments on a synthetic graph matching dataset demonstrates the scalability of our method to graphs with large number of nodes and its robustness to high partiality.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Many challenges from natural world can be formulated as a graph matching problem. Previous deep learning-based methods mainly consider a full two-graph matching setting. In this work, we study the more general partial matching problem with multi-graph cycle consistency guarantees. Building on a recent progress in deep learning on graphs, we propose a novel data-driven method (URL) for partial multi-graph matching, which uses an object-to-universe formulation and learns latent representations of abstract universe points. The proposed approach advances the state of the art in semantic keypoint matching problem, evaluated on Pascal VOC, CUB, and Willow datasets. Moreover, the set of controlled experiments on a synthetic graph matching dataset demonstrates the scalability of our method to graphs with large number of nodes and its robustness to high partiality. |
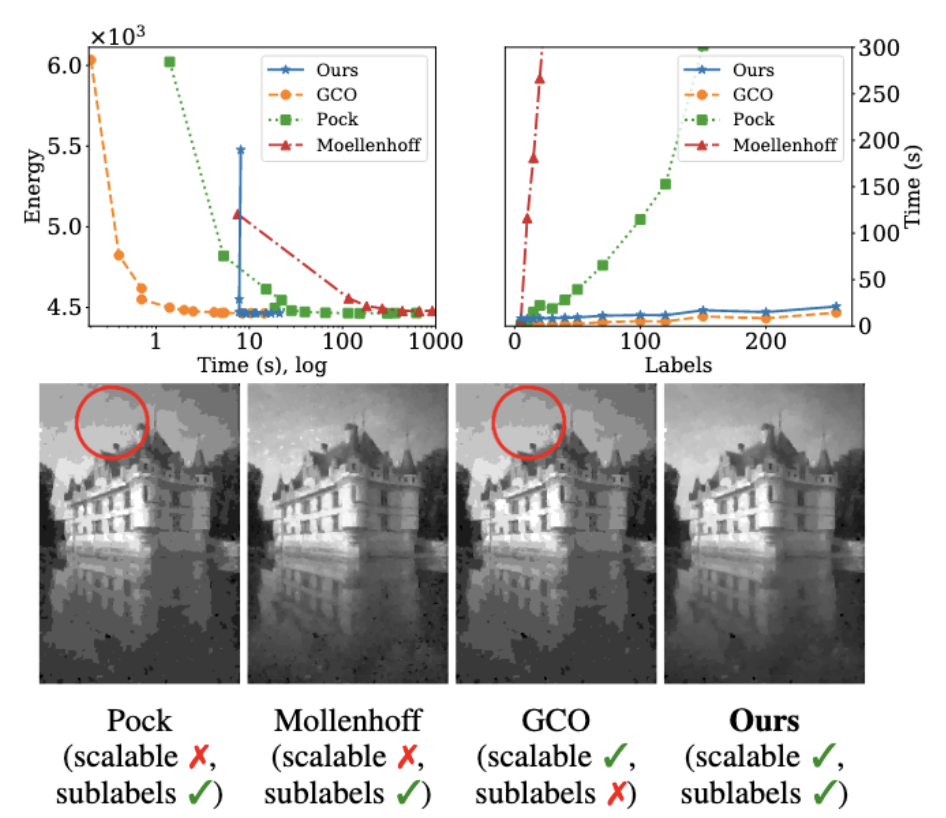 | Z. Nurlanov, D. Cremers, F. Bernard In: International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2022. [pdf] [code] @article{nurlanov2022b,
title = {Efficient and Flexible Sublabel-Accurate Energy Minimization},
author = {Z. Nurlanov and D. Cremers and F. Bernard},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.09596},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-05-17},
urldate = {2022-05-17},
journal = {International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR)},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
|



